Pressure vessels are enclosed containers engineered to hold gases or liquids at a pressure significantly different from the external atmosphere. They are crucial for industrial applications such as:
-
Gas storage: Holds gases like chlorine, nitrogen, and petroleum products.
-
Fluid storage: Used for fluids in industries such as chemical processing, petrochemical refining, and food and beverage.
-
Reactor vessels: Holds substances under high pressure and temperature for reactions (e.g., reactors in chemical plants or nuclear facilities).
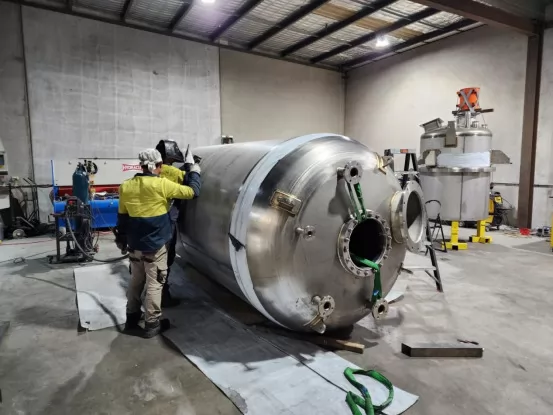

In the early 20th century, pressure vessels began to adopt designs with spiral steel reinforcements and reinforced welding techniques. These advancements allow vessels to withstand pressures over 10,000 psi, significantly enhancing their safety and durability.
-
Welding over Riveting: Initially, rivets were common in construction, but modern pressure vessels almost exclusively use welding due to the strength and integrity it provides.
-
Safety Improvements: Historical accidents highlighted the importance of precision and quality in manufacturing, prompting stringent standards in design and manufacturing processes.

Pressure vessels consist of the following components:
-
Cylinder: The main body, typically cylindrical, provides the bulk of the containment space.
-
Heads and End Caps: These are welded onto the ends of the cylinder to seal it.
-
Flanges: Connect different sections and allow access for maintenance.
-
Supports: Vertical or horizontal supports stabilize the vessel on its foundation.
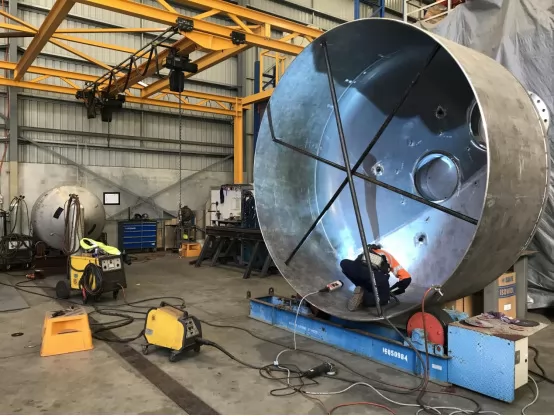

Manufacturing involves a sequence of processes to ensure precision and safety. Key steps include:
1. Material Preparation: Steel plates undergo rust removal, scaling, and surface treatment.
2. Marking and Cutting: Lines are drawn to guide cuts, and materials are shaped using mechanical or thermal cutting methods (e.g., plasma cutting).
3. Forming and Rolling: The cylinder is formed by rolling the plates, aligning them for longitudinal seams.
4. Welding: High-quality welding joins each part, especially in critical areas like longitudinal and circumferential seams.
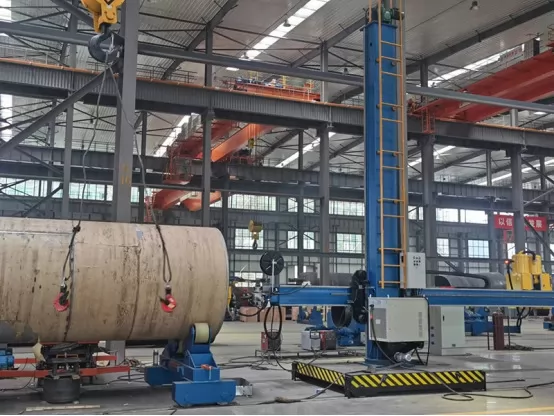

Your welding and positioning automation equipment plays a pivotal role in ensuring precision, efficiency, and safety in pressure vessel manufacturing. Here’s how:
Welding Rotators
Welding rotators hold and rotate the cylindrical vessel sections, allowing for:
-
Consistent Welding Speed: By adjusting the roller speed, the rotation speed is optimized for uniform welding, ensuring high-quality, uninterrupted weld seams.
-
Hands-Free Operation: The vessel can be rotated via remote control, reducing operator fatigue and minimizing handling risks.
-
Precision in Weld Positioning: Self-adjusting rotators automatically align with the cylinder size, providing seamless longitudinal and circumferential welds.
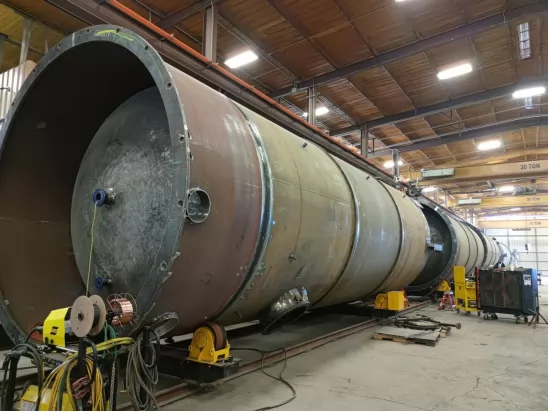

Positioning Manipulators
Positioning manipulators allow for precise adjustments of the workpiece, improving weld access and quality.
-
Vertical and Horizontal Adjustments: These manipulators lift, tilt, or rotate vessels to provide welders with optimal angles for difficult-to-reach areas.
-
High Load Capacity: Suitable for handling heavy components, manipulators are essential in large vessel manufacturing, reducing the need for manual repositioning.
-
Enhanced Safety: The automation reduces the manual handling of heavy vessels, minimizing accidents and ensuring alignment with regulatory safety standards.

Automated Welding Equipment
Automated welding technology in pressure vessel fabrication involves:
-
Consistent Quality: Automation allows precise, repeatable welds, ensuring that each joint meets strength and integrity standards.
-
Efficiency: Automated systems reduce the time required for setup and welding, significantly enhancing production rates.
-
Multi-Axis Control: Machines with multi-axis capability allow for complex welding operations, such as circumferential and longitudinal seams, without reorientation.

Comprehensive Benefits of Using Automated Equipment in Pressure Vessel Manufacturing
Implementing automation in pressure vessel production has several key advantages:
-
Enhanced Precision: Automated equipment minimizes human error, ensuring the vessel’s dimensions and welds are within strict tolerances.
-
Safety Improvements: Automation reduces the need for human involvement in hazardous tasks, such as handling large, heavy sections and welding in high-temperature environments.
-
Increased Throughput: Automated systems facilitate faster processing, reducing overall manufacturing time while maintaining quality.
-
Cost Efficiency: Although the initial investment is high, automated systems lower labor costs and reduce waste, improving profitability in the long term.

Safety and Quality Standards
Due to the hazardous nature of pressure vessels, adherence to safety standards is critical:
-
ASME Standards: Adhering to ASME guidelines for design, material selection, and construction ensures vessels withstand the intended pressure and usage.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Post-welding inspection methods such as ultrasonic testing, radiography, and dye penetrant testing ensure weld integrity and detect any defects.
-
Welding Procedures and Qualifications: Welders and procedures are certified per industry standards to ensure consistent and reliable workmanship.
Future Directions and Innovations
The future of pressure vessel manufacturing will likely see greater automation integration:
-
Robotics in Welding: Robots will increasingly handle complex welds, enhancing consistency and quality in high-stakes applications.
-
Smart Sensors and Monitoring: Pressure vessels equipped with smart sensors can continuously monitor conditions and detect potential issues before they escalate.
-
Advanced Materials: Research in materials like composite metals and corrosion-resistant alloys will enable vessels to withstand harsher environments and higher pressures.




.png)
.png)
.png)