.png)
.png)
.png)
This device is a TIG flange girth automatic welding machine designed according to the actual needs of customers. It is suitable for welding of pipe-flange, pipe-elbow, pipe-three-link, elbow-flange, pipe-pipe docking or angle connection. Adopt open tube pliers with patent technology, realize the automatic positioning and electric( manually) clamping of pipes, and stable rotation. The device mainly includes five parts: mechanical device part, program control welding power supply, wire delivery control system, arc horizontal swinging control system, welding auxiliary machine.
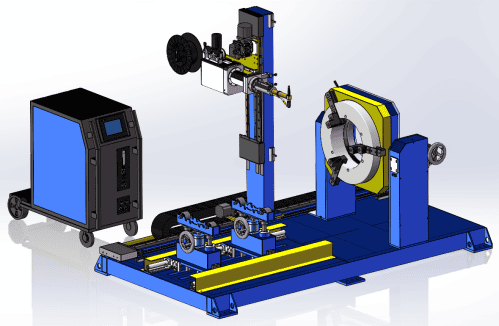
Effectively solve the problem of axial movement of the pipe;
Effectively reduce the problem of radial jump of the pipe;
Open design makes the long tube hanging easier and more convenient;
Electric three-claw step up, automatic attentive, reducing the difficulty of workers' operations;
AC servo motor driver, can have large speed adjustment range, fast response and high accuracy;
Gear/ sprocket transmission, high transmission efficiency, large carrying capacity, and can adapt to bad working conditions;
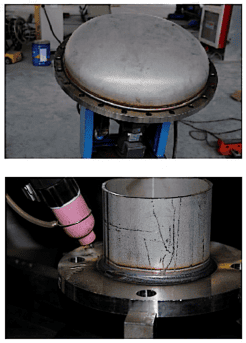

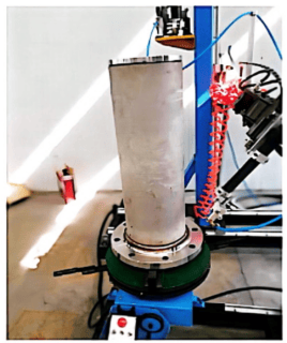

_1737011692_WNo_514d343.png)

Pipe automatic welding machines are specialized systems designed for high-precision and efficient welding of pipes. These machines are widely used in industries like oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, and construction, where high-quality welds are critical.
Deep penetration tungsten inert gas weld- ing(DP-TIG) is a new and efficient automatic welding process, which adopts a new welding method that can achieve"Keyhole" ( key- hole or small hole), combined with a special high-power welding torch, it solves the problems of traditional TIG arc stiffness, shallow penetration, and low welding efficiency.
1. Automate the welding process for pipes.
2. Support various welding techniques such as TIG (GTAW), Hot Wire TIG, MIG/MAG (GMAW), Plasma Arc Welding (PAW), and even SAW (Submerged Arc Welding) for specific applications.
3. Handle both circumferential (girth) and longitudinal welds.
1. TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas Welding)
Features:
High-quality, precise welds.
Suitable for thin-walled pipes or applications requiring minimal defects.
Commonly used for materials like stainless steel, titanium, and other alloys.
Applications: Nuclear power plants, food-grade pipelines, and aerospace.
2. Hot Wire TIG
Enhancement: Adds preheated filler wire to the TIG process, increasing deposition rate without compromising weld quality.
Advantages:
Higher productivity than conventional TIG.
Deeper penetration with controlled heat input.
Applications: Ideal for thicker pipes or high-deposition requirements.
3. MIG/MAG (Metal Inert/Active Gas Welding)
Features:
Faster than TIG, suitable for high-speed production.
Effective for non-critical welds or thicker materials.
Applications: Construction, shipbuilding, and automotive industries.
4. Plasma Arc Welding (PAW)
Features:
Highly concentrated arc for deeper penetration.
Excellent for thick materials or automation-friendly setups.
Applications: Heat exchangers, chemical processing equipment.
5. Hybrid Processes
Combines TIG with plasma, MIG, or laser welding to achieve high-quality, efficient welds.
1. Welding Head
Moves around the pipe to perform the welding process.
Equipped with precise controls for heat, wire feed, and gas flow.
Can include sensors for real-time monitoring of the weld pool.
2. Pipe Rotator/Positioner
Rotates the pipe for uniform welding, especially for circumferential welds.
Ensures stable welding for various diameters and thicknesses.
3. Control System
CNC or PLC-based control for precise parameter management.
Allows for programmable weld paths, speeds, and repeatable quality.
4. Wire Feeder
Provides a continuous wire feed, essential for TIG, MIG, or hot wire TIG processes.
5. Shielding Gas Supply
Argon, helium, or custom gas mixtures depending on the welding method and material.
6. Seam Tracking System
Uses laser or other sensors to ensure the welding torch aligns perfectly with the joint.
Oil & Gas Pipelines: Automated girth welding of pipes in the field or factory.
Power Plants: High-precision TIG or hot wire TIG for high-pressure piping systems.
Petrochemical Industry: Corrosion-resistant welds for stainless steel or alloy pipes.
Shipbuilding: Large-diameter pipe welding for structural and system integration.
Food & Pharmaceutical: High-purity pipe welding for hygiene-critical industries.
The arc energy is high, the stiffness is high, the weld penetration is large, and the penetration power is excellent. Medium and thick plates made of carbon steel, stainless steel, titanium alloy and other materials can be pen- etrated at one time, and the back is formed well;
High Efficiency: Faster welding cycles and reduced downtime.
High Efficiency: Especially critical for projects involving large numbers of welds.
Repeatable Quality: Automated systems ensure uniform welds, reducing human error.
Versatility: Can accommodate a wide range of diameters, thicknesses, and materials.
Cost Savings: Reduced labor costs and improved material utilization.
Real-Time Monitoring: Advanced systems include monitoring of weld pool, arc stability, and defects.
1. Lincoln Electric
2. ESAB
3.Fronius
4. Polysoude (specializes in orbital TIG and hot wire TIG systems)
5. Magnatech
6. MISA
1. Material Compatibility: Stainless steel, carbon steel, titanium, or alloy.
2. Pipe Dimensions: Diameter, wall thickness, and length.
3. Welding Speed: Based on production requirements.
4. Welding Environment: Factory or field.
5. Budget: Higher-end systems with advanced features (like seam tracking) may be more expensive but deliver better ROI.
|
Material |
Carbon steel, stainless steel |
|
|
Welding Technology |
Argon arc welding(TIG) |
|
|
Workpiece Size |
Diameter : |
Φ50~ Φ500mm |
|
Length : |
≤2000mm |
|
|
Wall thickness : |
≤3mm |
|
|
Weight : |
≤500KG |
|
|
Weld seam form |
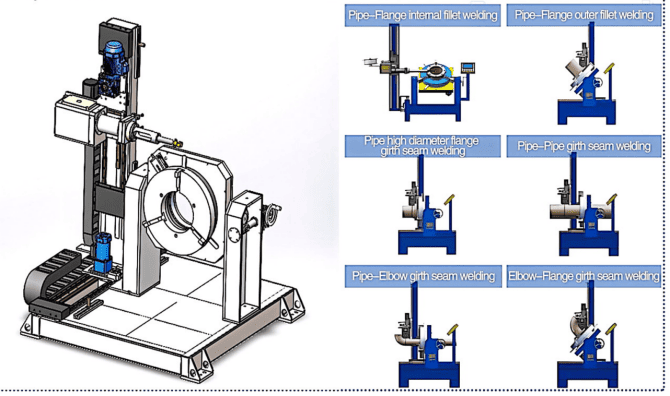
Pipe-Pipe、Pipe-Elbow、Pipe-Tee、Pipe-Flange、High neck flange |
|


|
Welding method |
1) Using a hollow chuck. 2) Circular seam welding: using a chuck to drive the workpiece to rotate. The method of fixing the welding gun. |
|
Welding technology |
TIG welding method is used for wall thickness ≤ 3MM; Equipped with multi-layer and multi pass welding function, welding 1-8 passes, each pass can be divided into 4 sections |
|
Protective gas |
TIG welding protective gas uses Ar (95%)+H2 (5%), and pure argon is used for both the shield gas and back protective gas: Ar 99.99% |
|
Welding wire specifications |
Φ1.2mm |
|
Group misalignment and group gap |
The 3mm wall thickness assembly should strive for zero misalignment and gaps, which can meet the requirements of TIG welding for single-sided welding and double-sided forming. It must be cut with a shearing machine (or laser) for cutting; Groove welding is required for walls with a thickness of 3mm or more. |
|
Weld cleaning |
Clean up oil stains, burrs, and other impurities within a 20mm range on both sides of the weld seam. |
|
Workpiece assembly |
Using manual TIG welding to fix the workpiece, the welding point length is about 5mm, the spot welding spacing is 50-100mm, and the fixing point head and tail are polished to achieve a smooth transition. |
|
Weld seam requirements |
The qualification level for radiographic testing shall not be lower than Level II, and the qualification level for penetrant testing shall not be lower than Level I; |
The circumferential seam welding special machine consists of a welding positioner, a lifting type welding rotator, a standard type welding rotator, a welding head, a welding power supply system, a control system, etc.
Equipment features:
1) This welding machine adopts TIG wire welding and hot wire welding processes.
2) The machine is equipped with a remote control box.
3) The switching of welding method (posture) is done manually.
4) The equipment layout adopts an integrated whole machine approach, which is conducive to stable operation of the equipment in low center of gravity situations.
5) The three-dimensional directional adjustment of the equipment adopts linear guide rails (double track guidance), AC motor drive, and gear rack transmission.
6) The equipment is equipped with arc voltage tracking (to meet the height direction tracking requirements during circumferential welding).
1)Circumferential welding
The operator lifts the spot welded workpiece onto the welding rotator (or a positioner + Elevating welding rotator) and manually locates the weld position through hand control. Press the start button to start arc welding, and the positioner rotates (the speed can be set on the program interface). The first step is argon arc welding as the base welding, and the second step is argon arc welding swing welding. After completing the welding of a single weld, manually move the welding gun to the next weld position and proceed with the welding of the next weld. After the welding is completed sequentially, the operator lifts off the workpiece.