.png)
.png)
.png)
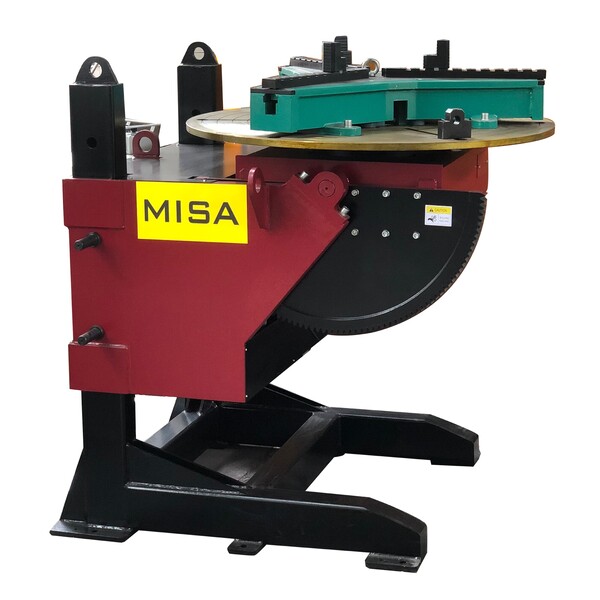

MISA MEWP-10 Elevating Welding Positioner feature all-fabricated-steel base construction. Tilting gear been quenched,ensure the strength. Rapid braking piece can in any position locking stability. With Slewing ring, ensure the safety and stable. The worktable is tilted by motor, accurate and reliable positioning. All electric conversion is frequency, so getting the big range of speed.
1Ton S.W.L Capacity
1200mm Table Diameter
0-90 Degree Tilting
2 Axis Rotation & Tilting, Manual Elevating
Wired Remote & Foot Panel / Wireless Remote Optional
CE/ UKCA/ CSA/ SGS



MISA MEWP-10 Elevating Welding Positioner feature all-fabricated-steel base construction. Tilting gear been quenched,ensure the strength. Rapid braking piece can in any position locking stability. With Slewing ring, ensure the safety and stable. The worktable is tilted by motor, accurate and reliable positioning. All electric conversion is frequency, so getting the big range of speed.
Various applications of pipe welding positioners are available, ranging from spooling pipes to positioning large cumbersome components like chassis components or structural steel.
It is very beneficial to use welding positioners when welding pipe, shafts, wheels, elbows and other fittings.
Positioning valves using pipe turning positioners is a common method for rotating or repositioning workpieces with a large offset load, as is the case with welding turntables.
The pipe welding positioners and welding rotating tables manufactured by MISA Welding & Cutting Automation are suitable for a wide variety of pipe handling applications.
Welding rotators and positioners are primarily used for manipulating and positioning workpieces during welding and fabrication processes. Here's how each equipment is typically used:
The welding positioners are use to manipulate workpieces to achieve precise welding angles and orientations, essential for complex geometries in industries like aerospace, automotive, and heavy equipment manufacturing.
Indeed, MISA Welding & Cutting Automation has a broad global footprint, supplying equipment across various continents including Europe, America, Asia, and Australia. Here are some highlights of their international reach:
Europe
- Industries Served: MISA supplies welding and cutting equipment to key industries such as automotive manufacturing, shipbuilding, and heavy machinery.
- Trade Shows: Participation in trade fairs like SCHWEISSEN & SCHNEIDEN in Germany helps MISA connect with European clients and showcase their latest products.
North America
- Industries Served: In North America, MISA's equipment is used extensively in oil and gas, construction, and aerospace sectors.
- Customer Base: They have built a strong customer base in the U.S. and Canada, known for their reliable and high-quality welding solutions.
Asia
- Regional Presence: MISA has a significant presence in Asian markets, including China, Japan, South Korea, and Southeast Asian countries.
- Local Partnerships: Collaborations with local distributors and direct sales strategies help them cater to the diverse needs of the Asian industrial sector.
Australia
- Mining and Resources: In Australia, MISA's equipment is crucial for mining operations, construction projects, and resource extraction industries.
- Adaptation: Their equipment is adapted to meet the specific requirements of the Australian market, ensuring compliance with local standards and regulations.

√ Standard match with CUL ,CE, SGS, UKCA certification
√ Professional design team
√ Motor power supply is equipped with safety protection
√ Perfect after-sales service
√ 13 months extended warranty.
Welding positioners made by MISA are all powered variable-speed machines that can rotate in either direction and can be controlled remotely by various switch options.
To work at the correct angle and a consistent surface, welders use welding positioners to hold a workpiece and rotate it.
With its fast rotation speed, it can support significant weight even when bearing a lot of weight.
Welding positioners are designed to ensure that the workpiece is always in the most advantageous welding position.

By eliminating waste in multiple aspects of their work, positioners improve productivity. The purpose of welding positioners is to ensure as much arc time as possible. In order to move cranes, chains, grippers and other types of rigging equipment effectively, welders often have to wait for the appropriate positioning of the workpiece, something that may have to be done more than once for one weldment. Positioners also make it possible for the welder to manipulate the part more quickly. Large parts can be positioned by one operator, eliminating the need for multiple people to reposition the part. As a result, there is a labor savings and employees are freed up for other tasks.

Welding positioners produce consistently high-quality welds, which is one of the major benefits.
It is difficult to produce quality welds when the part moves during the welding process.
If the material is securely fastened, sufficient penetration of the weld will be possible, as well as the ability to complete all welds without interruption.
In terms of weld quality, welding positioners solve many problems since they rotate the workpiece at a controlled rate and speed for a continuous, penetrating weld.

When selecting, operating, and maintaining a positioner, welders should consider these five suggestions, regardless of the size of the weldment.
- Confirm the center of gravity (COG)
It is important not only to take the weight and size of the weldment into account when selecting a positioning device, but also to consider how far the weldment's center of gravity is from the device. The center of gravity refers to the point at which the weldment balances on all axes equally. The point at which the weldment equalizes the pressure on each axis is the COG. The positioner is torqued more when the distance from the device increases. When welders add material and parts to a positioner, the COG changes, so these changes are important to consider.
Variable-speed motors control the table's rotation. It can be controlled either manually or automatically. Choosing the right positioner motor and control depends on the size and speed required for the desired welding operation.
Motor and control choices will be determined by the positioner manufacturer's specifications. A welder should make sure the capacity is adequate for the weldment by checking both horizontal and vertical load specifications. It is important that the positioning device can withstand as much force as possible.
- Connect the weldment correctly
This point in time is where the weldment would naturally separate from the positioning device, because that is where the weldment is attached. Fixtures for production are intended to be used repeatedly for a particular application. An automatic alignment fixture, such as this one, is permanently mounted to the positioner and is shaped so that it's easy to align parts.
The three-jaw chuck is often used to attach round parts. When the part is extended from the table, it should not pull away from the jaws. During and after the welding process, the part may expand or contract depending on how hot and how cold it is, which can affect the grip the chuck has on the part.
In sizing the positioning device, consider the weight and distance added by fixtures and chucks.
It is easy to understand how a weld positioner works - the device holds on to the particular workpiece by actively clutching and gripping it. When it moves and rotates, it will get into the position that a welder requires. You can imagine that it replaced the welder's hand in a more precise, accurate and automated way.
They're known as a surface, a part of a welding positioner that could properly hold hexagonal and round workpieces. The three-jaw welding chuck can be fixed on the table and clamp the workpiece firmly, and keep the position still when the workpiece rotates.

People don't see the differences between them; what makes them different?
In manual welding positioners, the turntable would need to be moved and rotated. It can either be controlled by a foot pedal or by a lever that you can manipulate by hand.
Welding positioners that work with extra accessories such as a torch or stand are called semi-automatic positioners.
Due to the fact that the positioner moves on its own, while the torch only stagnates, it's semi-automatic.
Automated weld positioners use robotics or automated movements to position welds.
In this positioner, the welding head and the rotator are controlled by machines, so no human intervention is needed.
In welding, positioning is not just for the weld's benefit - it offers a variety of advantages to the welder, as well.
To achieve the quality and quantity of welding needed, overhead welding is used.
By understanding what weld positioning does and how it is beneficial to welders, we can easily summarize how important it is.
The many benefits of weld positioning include the ability to meet required positions without moving and stabilizing the weld.
One of the benefits from the advantages above is that your welders are safer. How can it keep welders safe?
That is because of the characteristics of manual welding positioner:
People tend to believe that welding positioners can't be operated properly, but that's not true.
You can use it in the best and safest possible way by following these simple steps:
1. Put the positioner on a stable and flat surface to ensure your safety.
2. Choosing the rotational speed will save you from having to change it between welding.
3. Set up your welding equipment and make sure it's connected to a ground current.
4. Position the welding positioner horizontally at all times
If you follow these steps, you will never have issues with your manual weld positioner!
Torches aren't necessarily carried by welding positioners.
Using a welding positioner, a large workpiece is rotated to be welded.
Welding positioners are responsible for assisting with the positioning of the workpiece during welding.
You can weld certain materials with weld positioners if they can grasp or clutch them. Welding positioners are commonly used for welding the following materials:
When it comes to the particular workpieces that you'll be welding, welding positioners are not that picky.
Simply put, it is a rotary machine that can help you complete welding operations. The welding turntable is a device that can rotate the workpiece at a uniform speed. It can be controlled (manually) or set to automatic.

Example of what a welding turntable looks like
Welding positioner is a general term for equipment that can be used to assist you in completing your project.
The welding turntable is a kind of welding positioner. Its function is similar to a rotating table, so you don't have to worry about the positioning of the workpiece when welding.
In addition to the standard welding positioner can rotate, the faceplate can also be tilted to change the angle of the workpiece, which is more convenient for welding.

Using the welding positioner turntable is very simple. In fact, it can be classified into the following steps:
1. Before preparing for welding, load the workpiece on the workbench.
2. Then use a chuck and bolts to fix the workpiece on the worktable.
3. Use the hand control box or foot control box to start the rotation.
4. If you use a manual welding turntable, you must hold the filler metal and/or welding head. Otherwise, you can set them to execute at the speed you want.
5. Once it is over, you can unload the workpiece from the workbench; the welding is complete.
You can think of it as a machine that frees your hands from the workpiece.
Kindly Noted:
1. You can choose Fixed type or Elevating type ,Hydraulic type or any customized type of positioner
2. Welding Positioner can tilting from 0° to 120°, rotation 360° via VFD control.
3. Standard Voltage is 380V , 50HZ , 3PH. Customized from 220v to 600v.
4. Controlled is remote-control box, optional is foot switch and wireless remote.
5. If customer need more special requirements , we could study with our engineer.
FAQ:
1. What is the size of the faceplate?
The faceplate of the positioner can be selected according to the load capacity , or customized according to customer requirements. The faceplate has T-slots which can be used to fix the chuck.
2. What is the difference between the positioner and turning table?
The turning table can only rotation, and it is 1 Axis. The positioner can rotation and tilting, and it is 2 Axis. Customers can choose according to their needs.
We also have many types of positioners to choose from to meet the work needs of customers for different workpieces.
3. Can the positioner be used with a chuck?
Yes. There are some T-slots on the table to fix the chuck. T-slots can be customized according to the size of the chuck. And we can also provide the chucks you need.
4. Replacement parts can provide it?
We provide it for free during the warranty period, and charge for it after the warranty period.
5. Do you provide warranty?
We provide a 13-month warranty and can provide customers with technical guidance for life.
Welding manipulators and welding positioners are common equipment in industrial automation, mainly used to improve production efficiency and precision.
Welding manipulators are automated equipment, usually equipped with robotic arms and end effectors, capable of performing tasks such as grabbing, handling, and assembly. It is widely used in manufacturing, logistics, and medical fields.

Features of manipulators:
Positioners are used to adjust the position or angle of workpieces, and are usually used in conjunction with welding, spraying and other equipment to ensure that the workpiece is processed in the best position.
In modern industrial automation, the combined application of manipulators and positioners significantly improves production efficiency and accuracy. The manipulator is responsible for performing specific operation tasks, while the positioner is used to adjust the position and angle of the workpiece. The collaborative work of the two can achieve more complex production processes.

During the welding process, the manipulator is responsible for grabbing the welding gun and performing welding operations, while the positioner adjusts the position of the workpiece to ensure that the welding part is always at the best angle. This combination not only improves welding quality, but also reduces manual intervention.
The manipulator carries the spraying equipment for spraying, and the positioner rotates or moves the workpiece to ensure that the spray evenly covers all surfaces. This automated spraying method improves efficiency and reduces paint waste.
On the assembly line, the manipulator grabs and assembles parts, and the positioner adjusts the workpiece posture to ensure assembly accuracy. In the inspection link, the positioner rotates the workpiece, and the manipulator carries sensors for all-round inspection to improve inspection efficiency.
Advantages of using welding positioners and manipulators together
The coordinated application of manipulators and positioners not only improves production efficiency and quality, but also reduces labor costs. It is an indispensable combination in modern industrial automation. With the advancement of technology, this combination will play an important role in more fields.
Welding rotators and welding positioners are commonly used auxiliary equipment in the field of welding. Their main function is to support and adjust the position of the workpiece to improve the quality and efficiency of welding. Although their goals are the same, they differ in structure and application scenarios.
The welding rotator is mainly composed of a group of rollers. The rotation of the rollers drives the cylindrical or annular workpieces (such as pipes and cylinders) to rotate at a uniform speed, which is convenient for welding operations.

1. Applicable workpieces: Mainly used for long cylindrical or annular workpieces, such as pipes, storage tanks, cylinders, etc.
2. Function: The workpiece is driven to rotate at a uniform speed through the rotation of the rollers to achieve circumferential seam welding.
3. Operation method: Usually used in conjunction with an automatic welding machine, the welding gun is fixed and the workpiece rotates.
4. Advantages:
Typical application scenarios:
In some complex welding tasks, welding rotators and welding positioners can be used in collaboration. For example:
The welding rotator and the welding positioner each have their own unique advantages and application scenarios. The rotator is suitable for the circumferential welding of cylindrical workpieces, while the positioner is more suitable for multi-angle welding of complex workpieces. In actual production, selecting appropriate equipment according to the shape of the workpiece and welding requirements, or using them in coordination, can significantly improve welding efficiency and quality.
Whether it is a welding roller stand, a positioner or a welding manipulator, it can be integrated with the welding system.
Lincoln Electric: One of the largest and most respected welding companies in the world, offering a wide range of welding machines, consumables, and automation solutions.
Miller Electric: Known for its high-quality welding equipment, including MIG, TIG, and stick welders, as well as plasma cutters.
ESAB: A global leader in welding and cutting solutions, offering advanced equipment for various industries.
Fronius: Renowned for its innovative welding technologies, particularly in TIG, MIG, and arc welding.
Kemppi: A Finnish company known for its reliable and user-friendly welding machines and systems.
OTC Daihen: A Japanese brand specializing in welding robots and automation solutions.
Hypertherm: Famous for its plasma cutting systems, often used in conjunction with welding equipment.
Koike Aronson: A leading manufacturer of welding positioners, manipulators, and cutting systems.
Red-D-Arc: Provides welding positioners, manipulators, and other welding-related equipment for rent or sale.
Axis: Known for its welding positioners and turntables designed for precision and durability.
FIPA: Specializes in welding positioners and automation solutions for various industries.
Matsuo: A Japanese brand offering high-quality welding positioners and manipulators.
Yaskawa: While primarily known for robotics, Yaskawa also provides advanced positioning systems for welding applications.
Fanuc: A global leader in industrial robotics, including robotic welding systems.
ABB: Offers a wide range of robotic welding solutions and automation technologies.
KUKA: Known for its advanced robotic welding systems and automation solutions.
Panasonic: Provides robotic welding systems and welding equipment for various industries.
EWM: A German brand known for its high-performance welding machines and innovative technologies.
Lorch: Specializes in high-quality TIG and MIG welding machines.
Cigweld: An Australian brand off