.png)
.png)
.png)
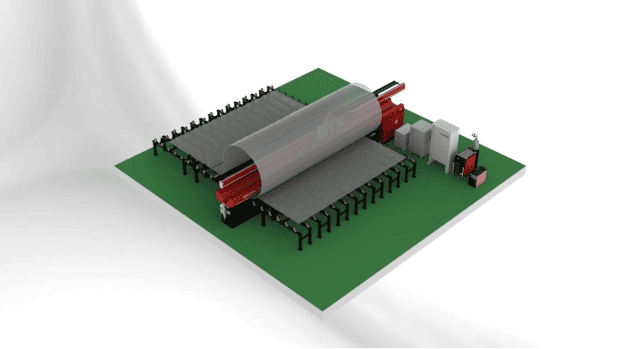
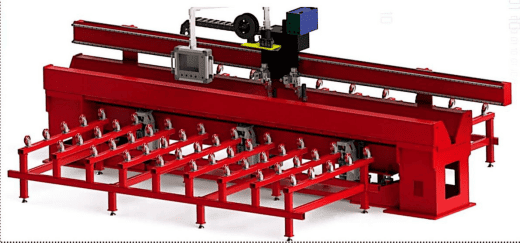
Splicing plates welding machine is mainly used for carbon steel, stainless steel, titanium alloy, aluminum and alloy flat docking. Suitable for tablets between 1.5-8mm flat, in the case of oblique cutting or milling, the thickness of the effect can reach 12mm. It can be equipped with TIG, MIG/MAG, PAW, SAW and other welding technology methods, the welding effect can be shaped up on both inside and outside by only welding on outside surface. The equipment structure is advanced, the welding process is reliable and effi- cient, and the entire control process is controlled by touch screens and PLC.
1. Suitable for splicing plates welding of thin plates with a thickness of 1.5-12mm;
2. Adopting piano-key compress method, the welding effect is good during heat dissipation, the workpiece deformation is small, and the welding quality is high;
3. Can be shaped up on both inside and outside by only welding on outside surface through the liner, and the best surface quality can be obtained through the front and back;
Plate-to-plate welding machines (also known as splicing plate automation welding machines) are specialized systems designed for joining large metal plates together, often used in industries where precision, efficiency, and high-quality welds are essential. These machines automate the splicing process to ensure consistent weld quality, minimize distortion, and increase productivity.
A longitudinal seam welding machine is an industrial welding solution designed for high-precision welding along the length (seam) of cylindrical, conical, or flat metal components. MISA’s longitudinal seam welder automates this process, delivering consistent, high-quality welds with minimal distortion – ideal for industries such as pressure vessels, HVAC, automotive, and food-grade containers.
Purpose: To automate the welding process for joining two plates edge-to-edge or overlapping, often used in heavy industries.
Applications: Widely employed in shipbuilding, construction, steel structure fabrication, wind towers, storage tanks, and pipeline projects.
Common Welding Techniques
Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)
TIG (GTAW)
MIG/MAG (GMAW)
Plasma Arc Welding (PAW)
Hybrid processes (e.g., SAW combined with MIG or laser welding).
1. Fully Automated Welding Control:
Supports TIG, MIG, MAG, and Plasma welding techniques.
Equipped with programmable logic controller (PLC) and touchscreen interface.
Reduces manual labor and ensures repeatable accuracy.
2. Pneumatic Clamping System:
High-pressure dual-sided clamping for secure workpiece positioning.
Minimizes weld deformation during the process.
3. Modular and Customizable Design:
Adjustable welding length, diameter, and thickness.
Easily integrated into automated production lines.
4. Superior Weld Quality:
Uniform weld seams without burn-through or overlap.
Designed for precision, even on thin-walled materials.
5. Operator-Friendly Interface:
Ergonomic control station with intuitive parameters.
Real-time feedback and fault diagnosis system.
1. Submerged Arc Welding (SAW):
High deposition rate and deep penetration.
Ideal for thick plates and long, straight seams.
Typically used for joining plates in shipyards or heavy industries.
2. TIG (GTAW) and Hot Wire TIG:
Precision welding with high-quality, defect-free welds.
Suitable for thin plates or applications requiring minimal distortion.
3. MIG/MAG (GMAW):
Faster than TIG, suitable for mild and stainless steel.
Common for general-purpose plate welding.
4. Plasma Arc Welding (PAW):
Highly concentrated arc for deep, narrow welds.
Suitable for both thin and thick plates, offering precise control.
5. Hybrid Welding:
Combines laser welding with SAW or MIG to increase speed and weld quality.
Useful for high-strength steel or aluminum plates.
1. Gantry or Frame:
Supports the welding head(s) and moves along the joint.
Provides stability and consistent weld quality.
2. Welding Head(s):
Equipped with the appropriate welding torch (TIG, MIG, SAW, etc.).
Often features multiple heads for tandem or twin-arc welding.
3. Plate Clamping System:
Secures the plates to prevent movement during welding.
Includes hydraulic clamps or vacuum systems for precise alignment.
4. Seam Tracking System:
Uses laser, camera, or sensor-based tracking to maintain perfect alignment with the joint.
5. Control System:
PLC or CNC-based system for programmable welding paths and parameters.
Allows customization of speed, heat input, wire feed rate, etc.
6. Flux Handling System (for SAW):
Automatically recovers and recirculates flux, ensuring efficiency and cleanliness.
7. Cooling System:
Water or air-cooled torches to handle high heat output in continuous operations.
Shipbuilding: Joining hull plates, deck sections, or superstructures.
Steel Fabrication: Manufacturing steel sheets for bridges, towers, and industrial structures.
Storage Tanks: Welding large plates for cylindrical or rectangular storage tanks.
Wind Towers: Fabricating cylindrical tower sections for wind turbines.
Efficiency: Reduces welding time and increases throughput for large-scale projects.
Quality: Consistent weld quality with minimal defects like porosity or undercut.
Reduced Labor: Automation minimizes the need for skilled manual welders.
Versatility: Capable of handling different materials (mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum) and thicknesses.
Cost-Effective: Saves time, labor, and material waste.




1. Initial Investment: High cost of machinery and setup.
2. Skill Requirement: Requires trained personnel to program and maintain the system.
3. Material Constraints: Limited to flat or slightly curved plates; highly contoured surfaces may require manual intervention.
1. ESAB: Known for high-performance SAW and automated welding solutions.
2. Lincoln Electric: Offers robust solutions for SAW and MIG/MAG automation.
3. Fronius: Specializes in advanced TIG and hybrid welding systems.
4. Koike Aronson: Renowned for plate processing and welding equipment.
5. Weldlogic: Focuses on precision TIG and plasma welding automation.
6. MISA: Excellent for SAW equipment and plate clamping systems.
If you are considering implementing or purchasing a plate-to-plate welding machine, let me know your specific project requirements (e.g., plate dimensions, materials, production volume) so I can provide tailored advice or recommendations!
|
Model |
PB3000 |
PB4000 |
PB6000 |
PB8000 |
PB1000 |
|
Max welding length(mm) |
3000 |
4000 |
6000 |
8000 |
10000 |
|
Welding plate thickness(mm) |
1.5-12 |
1.5-12 |
2.0-12 |
2.0-12 |
2.0-12 |
|
Max piano-key unilateral pressure(kgf/ cm) |
30 |
30 |
30 |
30 |
30 |
|
Adjustable range of piano-keý spacing width(mim) |
10-40 |
10-40 |
10-40 |
10-40 |
10-40 |
|
Moving mechanism speed(mm/ min) |
65-1250 |
65-1250 |
65-1250 |
65-1250 |
65-1250 |
|
Liner adjustment method and itinerary(mm/ min) |
Manual0-60 |
Manual0-60 |
Motorized0-60 |
Motorized0-60 |
Motorized0-60 |
|
Dimensions(L x Wx H mm) |
4650x1100x1550 |
5800x1100x1600 |
7900x1200x2000 |
10500x1200x1600 |
12000x1250x1600 |
|
Weight |
3.82 |
5.2 |
8.0 |
11.0 |
13.0 |
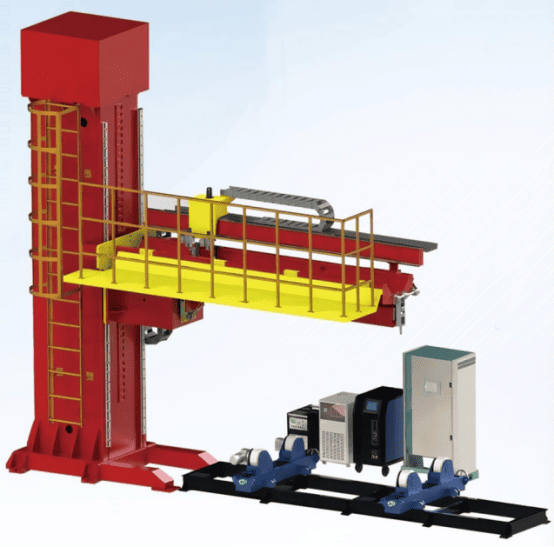
Longitudinal seam series welding tooling can be divided into various forms, mainly used for internal and external longitudinal seam welding of medium and thin-walled cylinders, and can be equipped with TIG,MIG/MAG, PAW and other welding processes. Suitable for welding carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum and its alloys, titanium and its alloys and other materials. It can be used for the welding of products such as food machinery, dyeing and finish- ing equipment, power switches, cylinders, medical machinery, special chemical containers, power pipelines, air conditioning machine casings, etc. And according to the specific conditions of the workpiece, this type of longitudinal seam tooling can be heightened and safety protection devices added. The welding process is reliable and efficient, and the entire welding process is programmed and controlled.

1. Adopting piano-key compress method, the welding effect is good during heat dissipation, the workpiece deformation is small, and the welding quality is high;
2. It can solve the welding of longitudinal seams of cylinders or plates within the thickness range of 0.4–12mm;
3. Can be shaped up on both inside and outside by only welding on outside surface through the liner, and the best surface quality can be obtained through the front and back;
4. Suitable for TIG, MIG/MAG, PAW,SAW and other welding process methods;
5. Can weld carbon steel, stainless steel, titanium alloy, aluminum alloy and other materials;
6. Specially customize the required equipment according to the struc- tural requirements of the workpiece;
 ’
’
A Lifting Type Longitudinal Seam Automation Welding Machine is an advanced welding system designed for high-precision longitudinal seam welding of metal plates, pipes, and cylindrical structures. Equipped with a vertical lifting mechanism, this machine ensures precise alignment and welding for a wide range of applications in industries like shipbuilding, pressure vessels, storage tanks, and wind tower manufacturing.
1. Vertical Lifting Mechanism:
Allows precise adjustment of the welding head height to accommodate different plate thicknesses and sizes.
Ensures consistent positioning of the welding torch for high-quality welds.
Smooth, motorized lifting for easy setup and operation.
Automation and Control:
Fully automated operation with programmable parameters for consistent results.
Equipped with a CNC or PLC-based control system for precise management of welding speed, voltage, current, and wire feed rate.
Seam Tracking System:
Integrated laser or optical seam tracking sensors maintain the welding torch’s alignment with the joint, compensating for any irregularities in plate positioning.
Real-time adjustments ensure uniform weld quality.
4. High Welding Versatility:
Compatible with multiple welding methods:
TIG (GTAW): Precision welding with minimal heat-affected zones.
Hot Wire TIG: Enhanced deposition rates and deeper penetration.
Submerged Arc Welding (SAW): High-speed welding for thicker plates.
MIG/MAG (GMAW): Cost-effective for general-purpose applications.
Plasma Arc Welding (PAW): For narrow and deep welds.
5. Plate Clamping and Backing System:
Hydraulic or pneumatic clamps secure the plates and provide stable support during welding.
Backing bars made of copper or ceramic prevent burn-through and improve weld pool control.
6. Cooling Mechanism:
Water-cooled or air-cooled torches manage heat efficiently during extended welding operations.
7. Robust Construction:
Heavy-duty steel frame ensures stability and durability, even in demanding industrial environments.
1. Pressure Vessel Manufacturing: Seam welding for cylindrical and rectangular tanks.
2. Storage Tank Fabrication: Joining large metal plates for liquid and gas storage tanks.
3. Wind Tower Production: Welding longitudinal seams of large steel segments for wind turbine towers.
4. Shipbuilding: Fabrication of ship hull plates and structural components.
5. Pipeline Manufacturing: Joining large-diameter pipes for oil, gas, and water transportation.
1. High Precision and Consistency: Automated operation and seam tracking deliver uniform, defect-free welds.
2. Increased Productivity: Reduces manual labor and production time, especially for large-scale projects.
3. Flexibility: Handles various materials (e.g., carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum) and thicknesses.
4. Minimal Distortion: Optimized heat input and secure clamping minimize warping and deformation.
5. Cost-Effective: Automation reduces labor costs and material waste.
Parameter Specification
Welding Processes TIG, Hot Wire TIG, SAW, MIG/MAG
Plate Thickness Range 2mm to 50mm
Plate Length Range 2m to 12m
Welding Speed 0.1 to 2 m/min
Torch Vertical Adjustment 500mm to 1000mm
Control System PLC or CNC
Power Supply 380V, 50Hz (customizable)
Cooling System Water-cooled or air-cooled
Seam Tracking Accuracy ±0.5mm
Clamping System Hydraulic or pneumatic
1. Plate Positioning and Clamping:
Plates are loaded onto the machine and aligned edge-to-edge.
The hydraulic/pneumatic clamps secure the plates to prevent movement.
2. Torch Adjustment:
The lifting mechanism adjusts the welding torch height to match the plate thickness.
Seam tracking sensors align the torch with the joint.
3. Welding Process:
The machine initiates the programmed welding process and moves the welding head along the seam.
Real-time adjustments ensure uniform penetration and bead quality.
4. Cooling and Unloading:
The cooling system prevents overheating during welding.
Once the welding is complete, the clamps release the plates for unloading.
1. Plate Positioning and Clamping:
• Plates are loaded onto the machine and aligned edge-to-edge.
• The hydraulic/pneumatic clamps secure the plates to prevent movement.
2. Torch Adjustment:
• The lifting mechanism adjusts the welding torch height to match the plate thickness.
• Seam tracking sensors align the torch with the joint.
3. Welding Process:
• The machine initiates the programmed welding process and moves the welding head along the seam.
• Real-time adjustments ensure uniform penetration and bead quality.
4. Cooling and Unloading:
• The cooling system prevents overheating during welding.
• Once the welding is complete, the clamps release the plates for unloading.
1. Oil & Gas: Pipelines, pressure vessels, and storage tanks.
2. Energy: Wind towers and thermal plant components.
3. Construction: Structural steel plates for bridges, buildings, and heavy machinery.
4. Shipbuilding: Hull plates and large structural elements.
5. Aerospace: Precision welding of lightweight and high-strength alloys.
• Enhanced Flexibility: Accommodates a wide range of plate sizes, thicknesses, and materials.
• Improved Quality: Consistent and defect-free welds with advanced seam tracking.
• Increased Productivity: High-speed automation for faster project completion.
• Cost Efficiency: Reduced labor costs and material waste.
|
Model |
ZFS 3000 |
ZFS 4000 |
ZFS 5000 |
|
Max Welding length(mm) |
3000 |
4000 |
5000 |
|
Max Clamp length(mm) |
3100 |
4160 |
5250 |
|
Clamp Diameter (mm) |
Ø450-3000 |
Ø450-4000 |
Ø450-5000 |
|
Clamp Thickness(mm) |
1.0-10 |
1.5-10 |
2.0-10 |
|
Press plate Max Clamp capacity(kgf/cm) |
30 |
30 |
30 |
|
Adjustable range of pressure finger width(mm) |
5-40 |
10-40 |
10-50 |
|
Vertical travel of the core shaft (mm) |
30 |
50 |
50 |
|
Walking cart speed (mm/min) |
65-1250 |
||


Our longitudinal seam welder supports as thin as 0.5 mm, suitable for applications like stainless steel containers and pipes.
Yes, the machine is compatible with aluminum. We recommend using MIG welding or AC TIG for optimal results on aluminum materials.
Absolutely. We offer customization based on your production requirements, from 600 mm to over 3,000 mm.
Standard delivery is 6–8 weeks, depending on configuration. Expedited production is available for urgent orders.
Yes. Depending on the welding process, air-cooled or water-cooled torches are available for thermal control.
Yes, it’s fully compatible with robotic arms, conveyors, and automated inspection systems.
MISA's Pipe Flange Welding Machine