1. “Welding Rotators: Enhancing Efficiency and Safety in Industrial Welding”
Welding rotators are essential tools in industrial welding, designed to rotate and position workpieces for better access and precision during welding operations.
Efficiency Improvements
– Reduction in Manual Handling: Welding rotators automate the rotation of workpieces, significantly reducing the need for manual adjustments and handling. This streamlines the workflow and minimizes downtime.
– Consistency and Quality of Welds: By maintaining a consistent rotation speed and position, welding rotators ensure uniform weld quality across the entire workpiece.
– Speed and Productivity Gains: Automated rotation speeds up the welding process, allowing for quicker completion of tasks and higher production rates.
Safety Enhancements
– Reduced Risk of Injuries: Automation minimizes the physical strain on workers, reducing the risk of repetitive strain injuries and other manual handling-related injuries.
– Stable and Secure Clamping: Welding rotators provide a stable platform for workpieces, ensuring they remain securely in place during welding, which enhances overall workplace safety.
Welding rotators play a crucial role in improving efficiency and safety in industrial welding. As technology advances, these tools continue to evolve, offering even greater benefits.
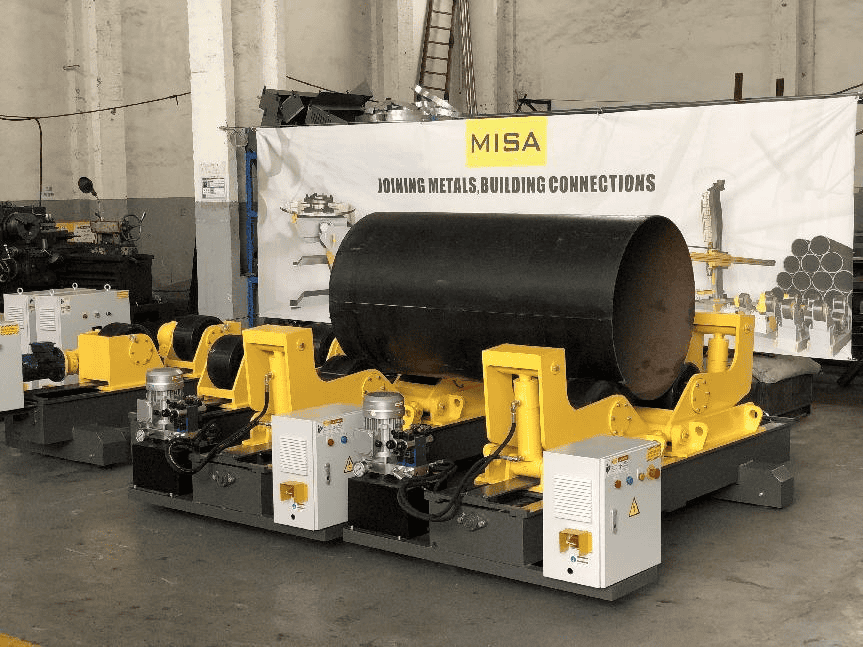

2. “Types of Welding Rotators: Conventional vs. Self-Aligning Rotators”
Welding rotators come in various types, each suited for different applications. Understanding the differences between conventional and self-aligning rotators is crucial for making the right choice.
Conventional Welding Rotators
– Features and Characteristics: Conventional rotators typically require manual adjustment to fit different workpiece sizes. They are robust and can handle heavy loads.
– Applications and Advantages: Ideal for large, uniform workpieces in industries like shipbuilding and pressure vessel fabrication.
– Limitations: Manual adjustments can be time-consuming and less efficient for irregularly shaped workpieces.

Self-Aligning Welding Rotators
– Features and Characteristics: These rotators automatically adjust to accommodate different workpiece diameters, reducing setup time and ensuring optimal alignment.
– Applications and Advantages: Suitable for a variety of workpiece shapes, including irregular ones. Commonly used in industries with frequent changes in workpiece sizes.
– Limitations: Generally more expensive than conventional rotators and may have higher maintenance needs due to the complexity of their mechanisms.
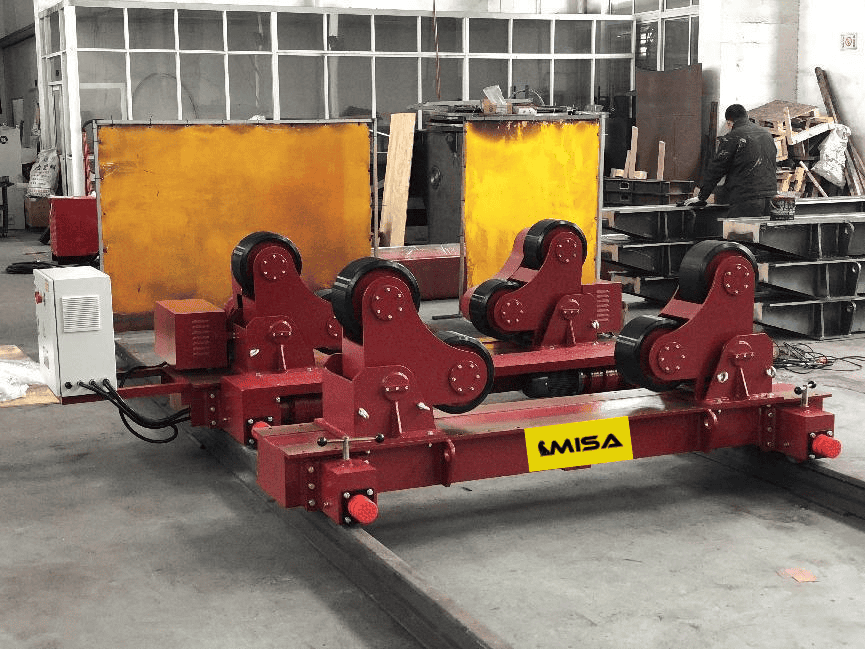
Comparison between the two
– Key Differences: Manual vs. automatic adjustments, cost, and suitability for different workpiece shapes.
– Situational Suitability: Conventional rotators are best for consistent, heavy-duty tasks, while self-aligning rotators are ideal for diverse and changing workloads.
Selecting the right type of welding rotator depends on your specific needs and project requirements. Both types offer unique advantages that can enhance productivity and efficiency.
3. “Top Features to Look for in a Welding Rotator”
Choosing a welding rotator with the right features is essential for ensuring optimal performance and meeting specific project requirements.
Load Capacity
– Importance: The load capacity must match the weight of the workpieces to ensure safe and efficient operation.
– Considerations: Overloading can damage the rotator and compromise safety.
Rotation Speed
– Adjustable Speeds: Different welding processes may require varying rotation speeds. Look for rotators with variable speed controls.
– Impact on Welding Quality: Consistent and appropriate speed helps maintain weld quality and prevents defects.
Durability and Construction
– Materials Used: High-quality materials like steel and polyurethane rollers enhance the durability of the rotator.
– Lifespan: Durable construction reduces maintenance needs and extends the equipment’s lifespan.
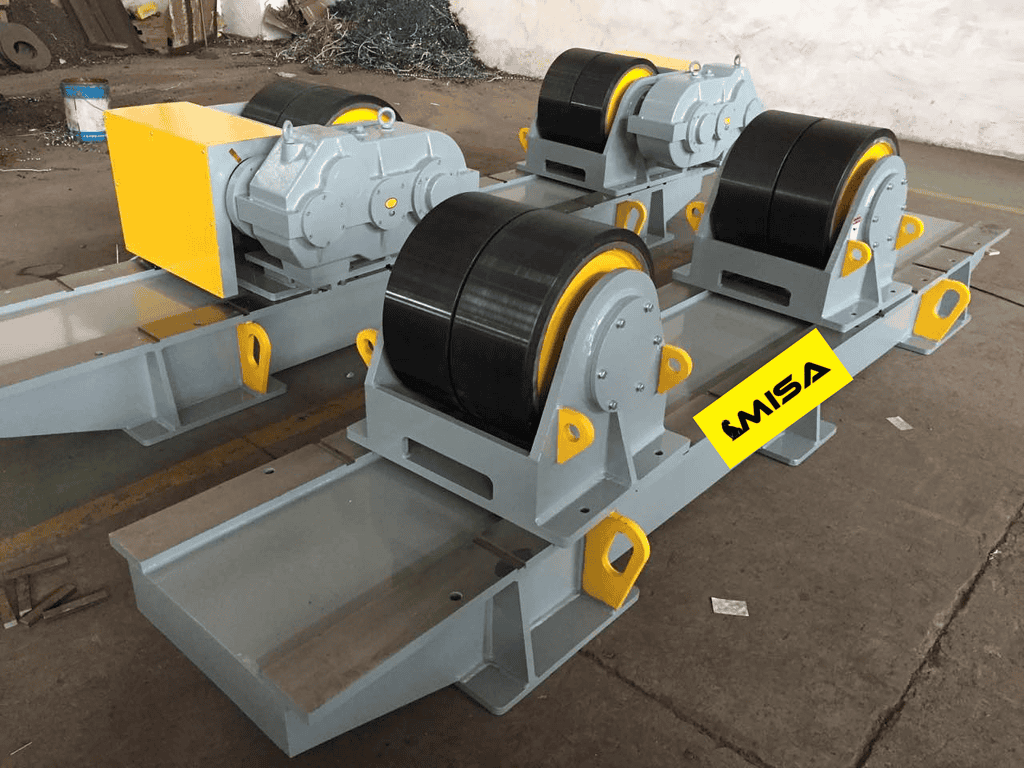
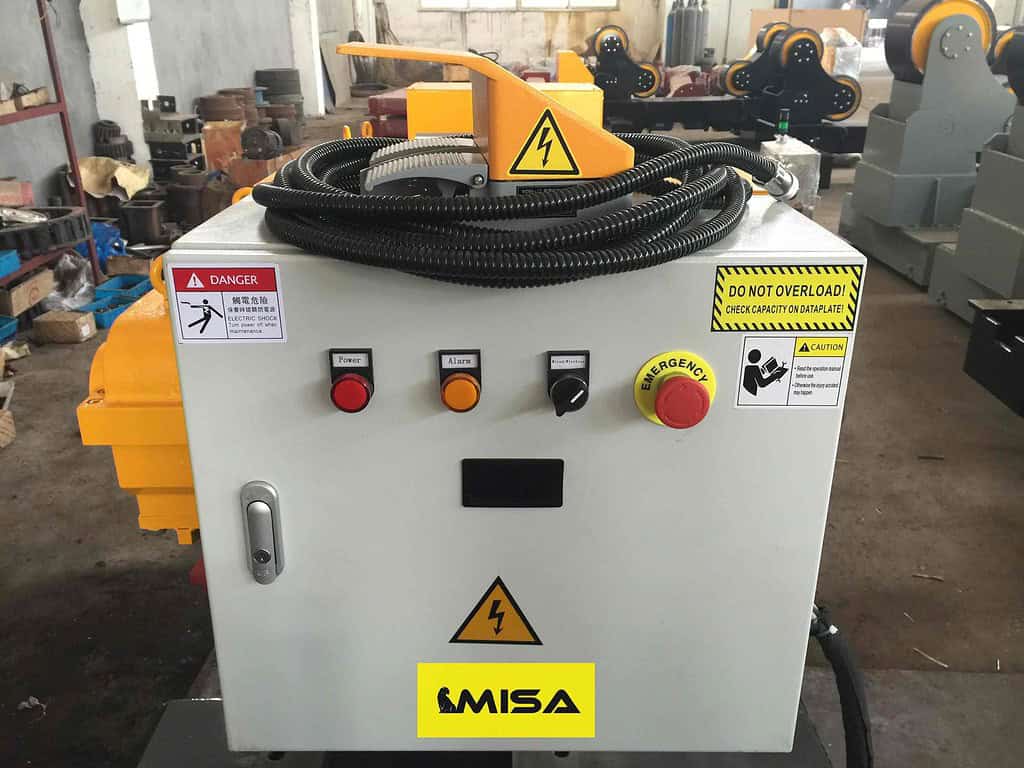
Safety Features
– Essential Safety Features: Look for emergency stop buttons, protective shielding, and overload protection.
– Operator Safety: Enhanced safety features protect operators from potential hazards.
Selecting a welding rotator with the right features can significantly improve your welding operations, ensuring both efficiency and safety.

4. “How to Choose the Right Welding Rotator for Your Project”
Choosing the right welding rotator involves evaluating your project requirements and understanding the available options.
Project Requirements
– Assessing Workpiece Size and Weight: Determine the dimensions and weight of the workpieces to select a rotator with adequate load capacity.
– Determining Welding Processes Used: Different welding processes may have specific requirements for rotation speed and stability.
Rotator Specifications
– Matching Specifications to Project Needs: Ensure the rotator’s specifications align with your project’s demands, such as load capacity, rotation speed, and clamping mechanisms.

Budget Considerations
– Balancing Cost and Features: Evaluate the cost against the benefits offered by various models. Higher initial investment may lead to long-term savings through improved efficiency.
Manufacturer and Brand Reliability
– Importance of Choosing Reputable Brands: Opt for manufacturers with a track record of quality and reliability to ensure the longevity and performance of the rotator.
Conclusion
Recap and Final Tips for Selecting the Right Rotator: Consider all factors to make an informed decision that enhances your welding operations.

5. “Applications of Welding Rotators in Various Industries”
Welding rotators are versatile tools used across multiple industries to improve welding processes.
Automotive Industry
– Uses in Manufacturing Exhaust Systems, Fuel Tanks, etc.: Rotators ensure precise welding of cylindrical components, enhancing product quality and consistency.
Aerospace Industry
– Applications in Welding Aircraft Fuselages, Rocket Components: High precision and reliability are critical in aerospace, and rotators help achieve these standards.

Construction Industry
– Welding Steel Reinforcement Bars, Structural Beams: Rotators facilitate efficient and accurate welding of large and heavy construction components.
Medical Device Industry
– Manufacturing Implantable Devices, Surgical Tools: Precision and consistency are vital in medical device manufacturing, making rotators indispensable.
General Manufacturing
– Uses in Various Manufacturing Processes: From bicycles to industrial machinery, welding rotators are used to weld cylindrical and curved components efficiently.

Conclusion
Summary of Industry Applications: Welding rotators play a crucial role in enhancing productivity and quality across diverse industries.
6. “Maximizing Productivity with Automated Welding Rotators”
Automation in welding significantly boosts productivity and consistency. Automated welding rotators are key to achieving these improvements.
Benefits of Automated Welding Rotators
– Increased Production Speed: Automation reduces manual intervention, speeding up the welding process.
– Reduced Manual Intervention: Less need for manual adjustments minimizes downtime and enhances efficiency.
– Consistent Weld Quality: Automated systems maintain consistent parameters, ensuring high-quality welds.
Key Features
– Integration with Automated Systems: Automated rotators can be seamlessly integrated with robotic and other automated welding systems.
– Adjustable Settings for Different Tasks: Flexibility to adjust settings for various welding tasks increases versatility and efficiency.
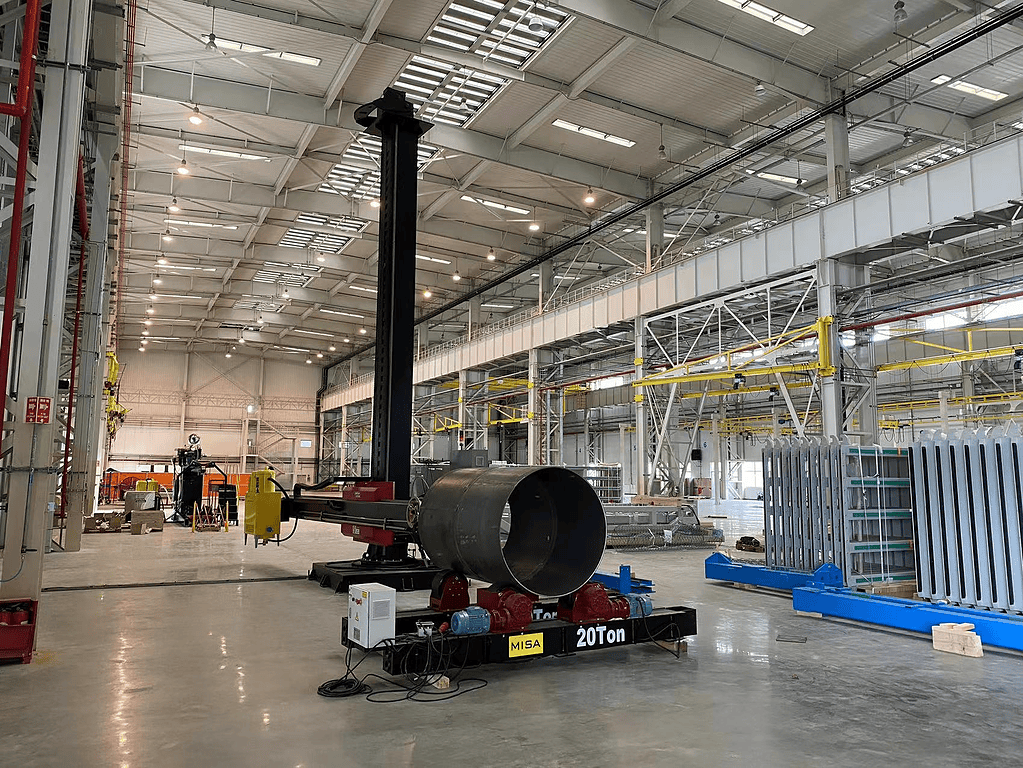
Summary of Productivity Benefits: Automated welding rotators are essential for modern, high-efficiency welding operations.
7. “Maintenance Tips for Prolonging the Life of Your Welding Rotator”
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of welding rotators.
Daily Maintenance
– Routine Checks and Cleaning: Regular inspection and cleaning to prevent buildup of debris and ensure smooth operation.
Periodic Maintenance
– Lubrication, Part Replacements, and Adjustments**: Periodic lubrication and timely replacement of worn-out parts to maintain efficiency and prevent breakdowns.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
– Identifying and Addressing Common Problems: Tips for diagnosing and fixing common issues such as misalignment, uneven rotation, and mechanical wear.
Safety Checks
– Ensuring All Safety Features Are Functional: Regular testing of safety features like emergency stops, clamping mechanisms, and shielding to protect operators.
Recap and Importance of Consistent Maintenance: Proper maintenance practices can extend the lifespan of welding rotators and ensure safe, efficient operation.
8. “Buying Guide: Top Welding Rotator Brands and Models”
– Choosing the correct brand and model of welding rotator is important.
Choose a brand that has reputation and reliability in the industry.
– Comparison of Popular Models and Their Features: Detailed comparison of features, load capacities, rotation speeds, and clamping mechanisms.
– Highlight the strengths and weaknesses of each model.
– Insights from customer reviews and feedback on various models. Common themes in feedback, such as durability, ease of use, and customer service.
– Factors to consider when buying a welding rotator, such as budget, project requirements, and brand reputation. Also Additional Features to Look For. Important features that can enhance performance and safety.
Summary of key points and recommendations for choosing the best welding rotator for your needs.
