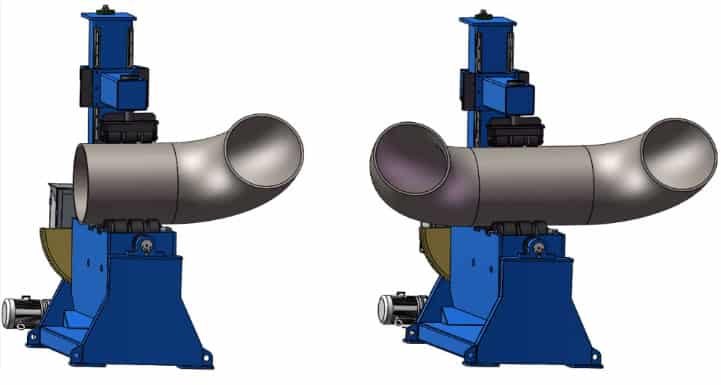
1. Introduction
– Definition of Welding Rotators
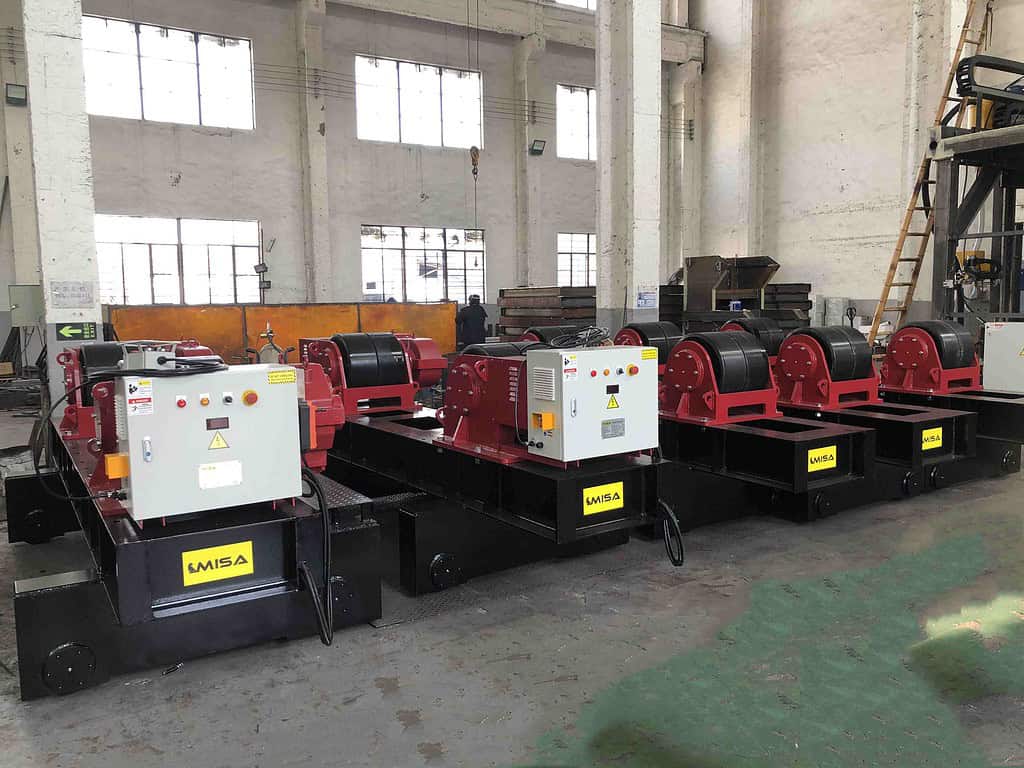
Welding rotators are mechanical devices used to rotate cylindrical workpieces, such as pipes and tanks, to facilitate the welding process. They come in various configurations to accommodate different sizes and types of workpieces, ensuring smooth and continuous rotation for high-quality welds.
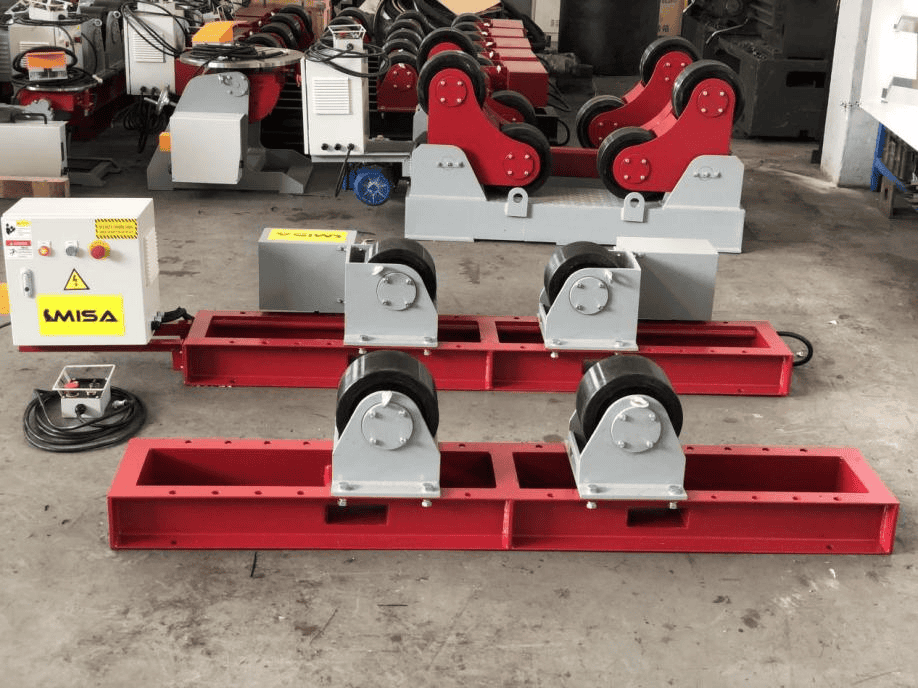
– Importance in Welding and Fabrication Processes
Welding rotators play a crucial role in modern welding and fabrication by improving efficiency, precision, and safety. They allow for automated and consistent welds, reducing the need for manual handling and minimizing errors. This leads to increased productivity and better overall weld quality.
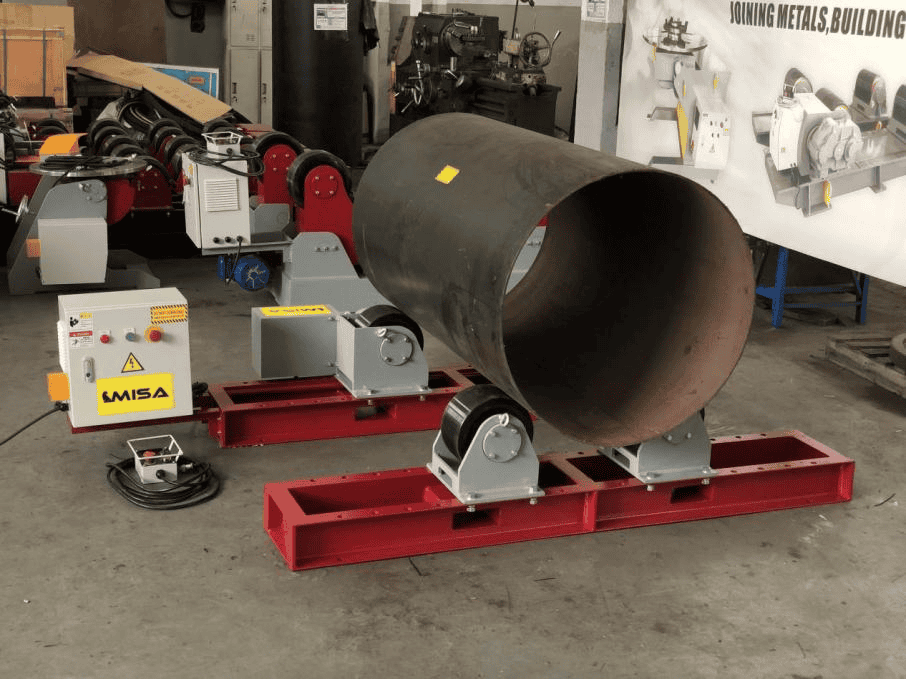
– Overview of Different Applications
Welding rotators are used across various industries, including petrochemical, oil and gas, shipbuilding, and power generation. They are essential for welding pressure vessels, heat exchangers, tanks, and other cylindrical structures that require precise and uniform welds.

2. Types of Welding Rotators
– Conventional Welding Rotators
Description and Features: Conventional rotators use fixed roller beds and require manual adjustment to align with different workpiece diameters.
Advantages and Disadvantages: They are durable and suitable for heavy-duty applications but can be time-consuming to adjust.
Typical Applications: Used in industries where workpiece sizes are consistent or adjustments are infrequent.
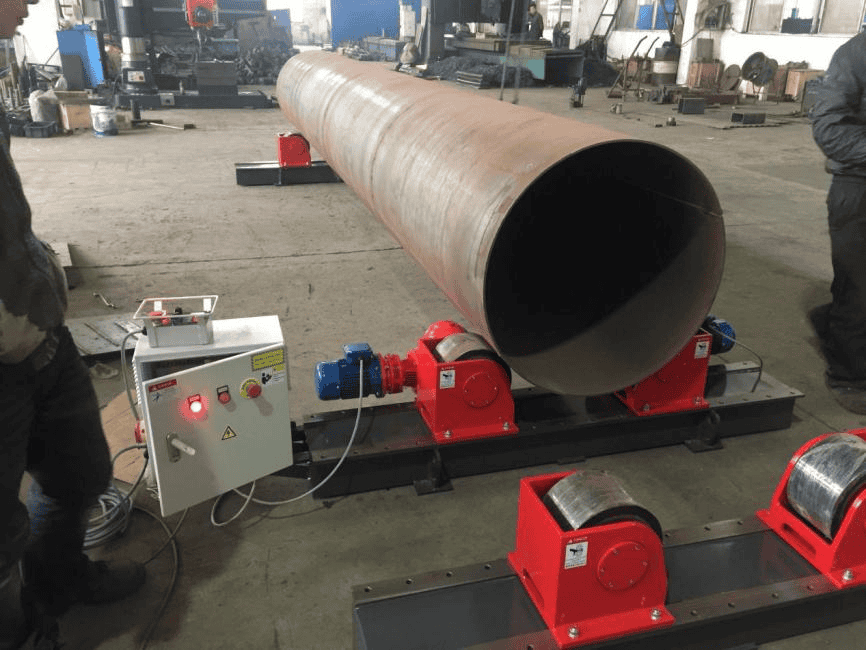

– Self-Aligning Welding Rotators
Description and Features: These rotators automatically adjust to the diameter of the workpiece, providing a hassle-free setup.
Benefits Over Conventional Rotators: They save time and reduce manual labor, making them ideal for variable diameter workpieces.
Use Cases in Various Industries: Common in industries with frequent changes in workpiece sizes, such as pipe manufacturing and repair.
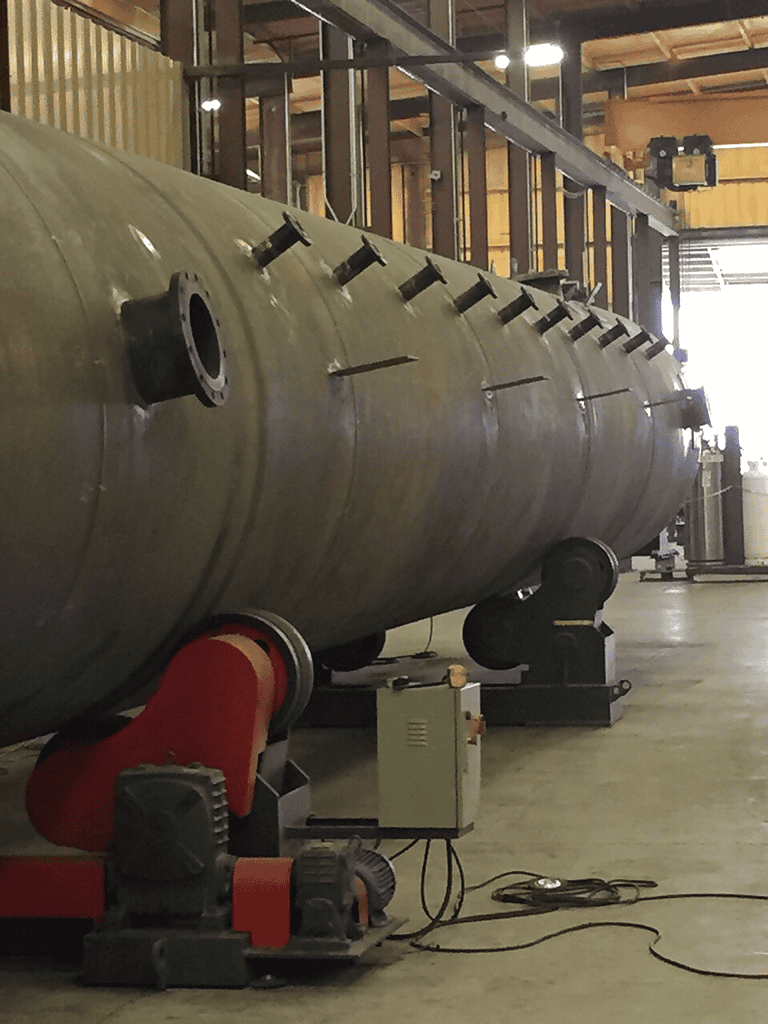
– Fit-Up Welding Rotators
Description and Features: Fit-up rotators allow for precise alignment and positioning of workpieces before welding.
Specific Benefits and Applications: They ensure high accuracy and are used in applications requiring exact weld positioning.
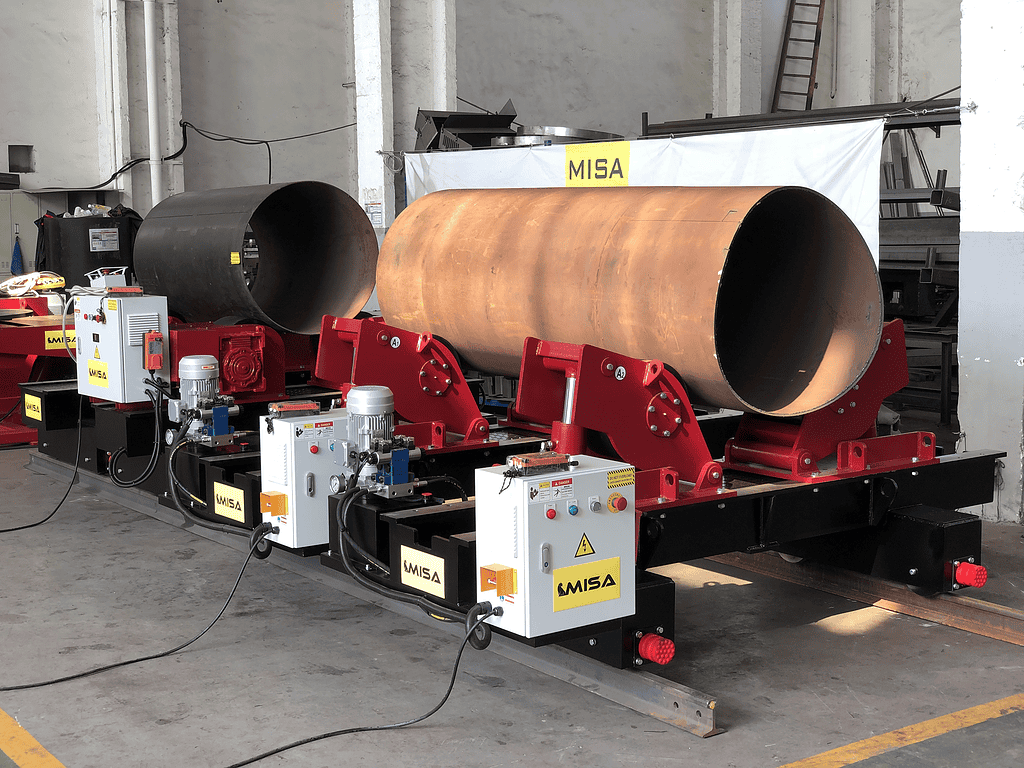
– Pipe Pinching Rotators
Description and Features: These rotators clamp onto pipes, providing secure rotation for welding.
Ideal Scenarios for Use: Best for applications where the workpieces need to be firmly held in place during welding, such as in pipeline construction.
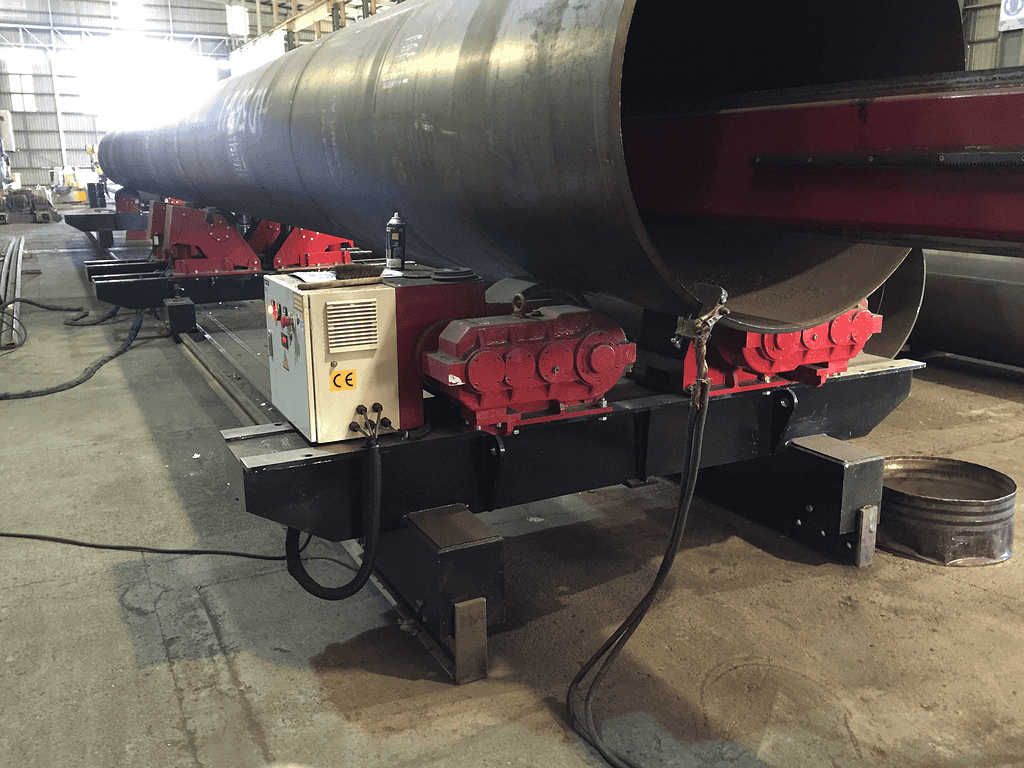
3. Key Features and Specifications
– Load Capacity
Range of Load Capacities: Welding rotators come with various load capacities, from a few hundred kilograms to several tonnes.
How to Determine Required Capacity: Consider the weight and size of your workpieces to choose a suitable rotator.


– Roller Types
Rubber vs. Steel Rollers: Rubber rollers provide better grip and reduce the risk of damage to the workpiece, while steel rollers are more durable and suitable for heavy loads.
Impact on Performance and Application: The choice of roller material affects the rotator’s performance and suitability for different applications.

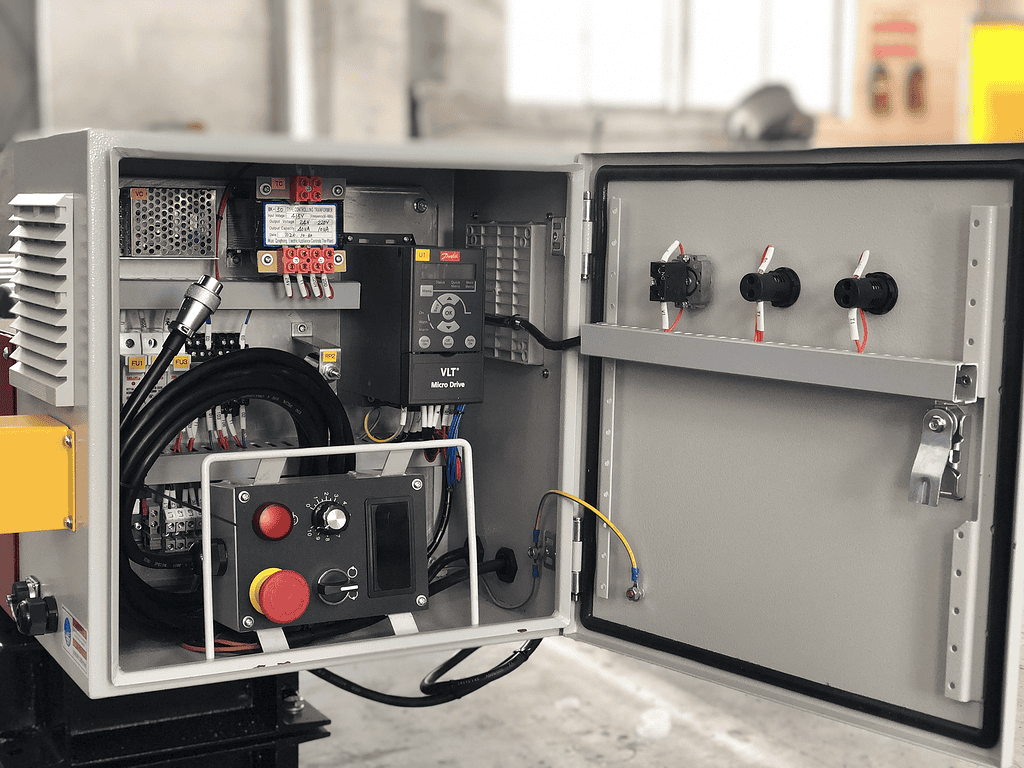
– Control Systems
Manual vs. Automated Controls: Manual controls offer simplicity and reliability, while automated systems provide precision and ease of use.
Integration with Other Welding Equipment:** Ensure the control system is compatible with your existing welding setup for seamless operation.
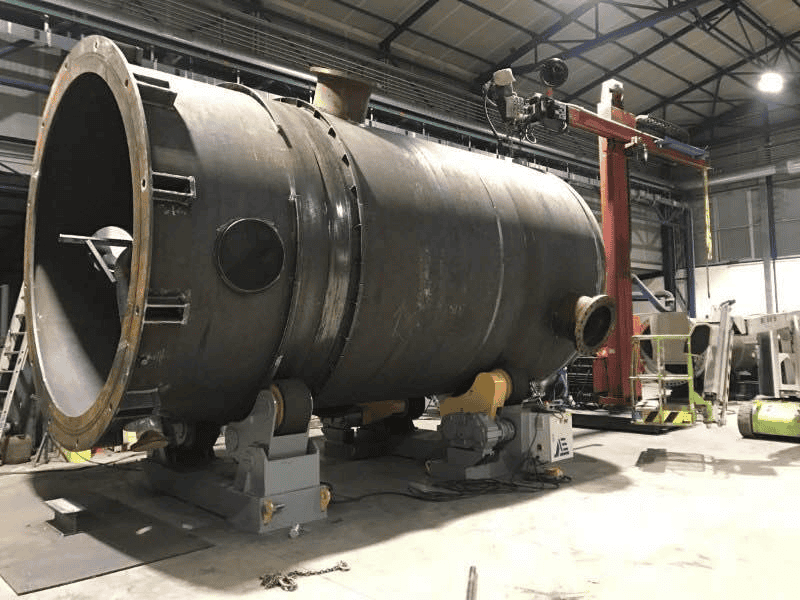
4. Applications of Welding Rotators
– Pressure Vessels
Importance in Fabrication: Welding rotators are essential for fabricating pressure vessels, ensuring uniform welds and structural integrity.
Specific Rotator Requirements: High load capacity and precise control are crucial for handling large and heavy pressure vessels.
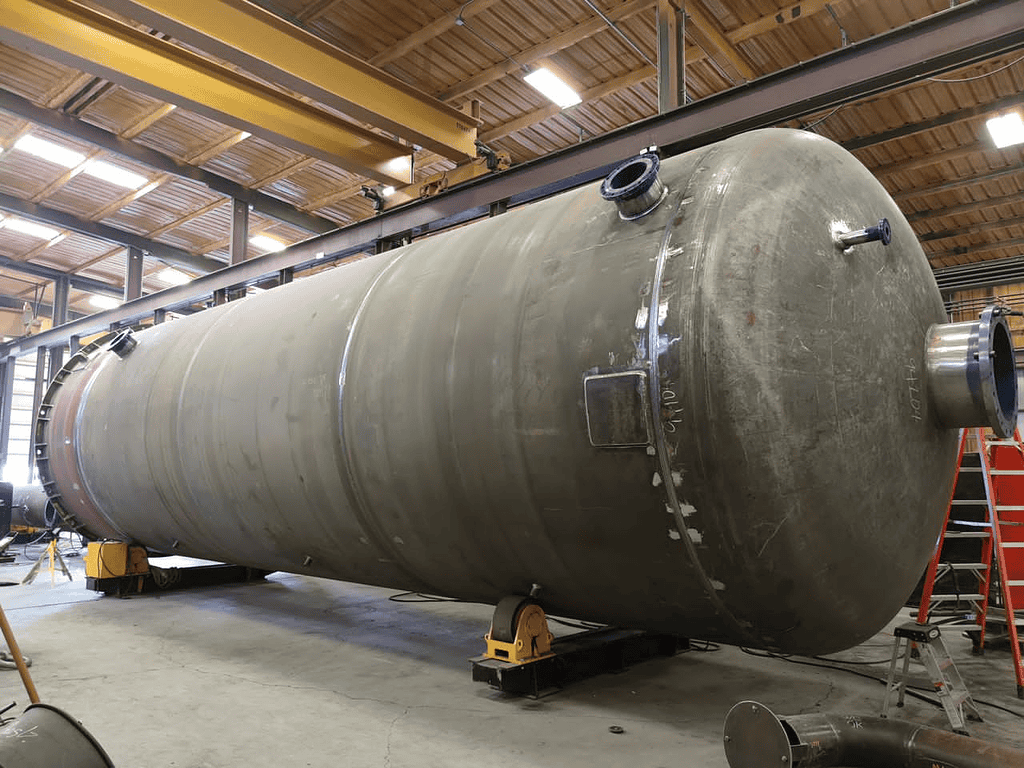
– Tanks and Cylindrical Vessels
Types of Tanks Commonly Welded: Storage tanks, water tanks, and chemical tanks.
Benefits of Using Rotators: They provide stable and consistent rotation, improving weld quality and reducing production time.

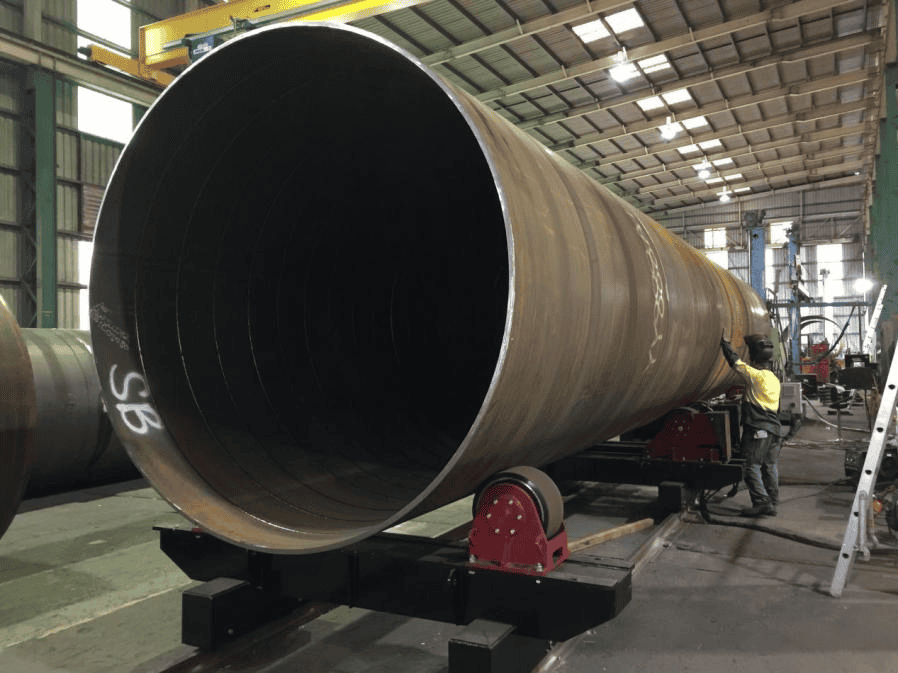
– Pipes and Piping Systems
Common Industries Using Pipe Rotators: Oil and gas, petrochemical, and water treatment industries.
Enhancing Welding Precision and Efficiency: Pipe rotators ensure accurate and consistent welds, enhancing the overall efficiency of the welding process.
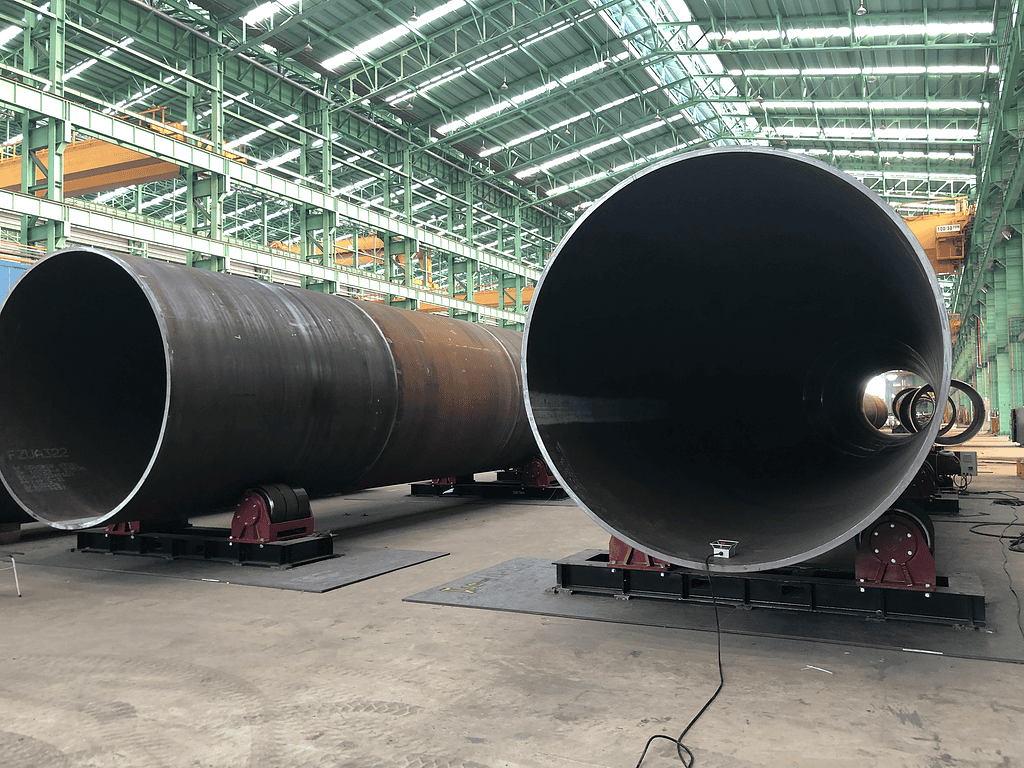
– Shipbuilding
Applications in Building and Repairing Ships: Welding rotators are used for fabricating and repairing ship components, such as hulls and pipelines.
Impact on Productivity and Safety:** They reduce manual handling, improve safety, and increase the speed of production.

5. Benefits of Using Welding Rotators
– Increased Productivity
How Rotators Speed Up Welding Processes: Automated rotation allows for continuous welding, reducing downtime and increasing output.
– Improved Weld Quality
Consistency and Precision in Welding: Rotators provide uniform rotation, resulting in higher quality and more consistent welds.
– Enhanced Safety
Reducing Manual Handling and Worker Fatigue: Automation minimizes the need for manual intervention, reducing the risk of injuries and worker fatigue.
– Cost Efficiency
Long-Term Savings and ROI: While the initial investment in welding rotators can be high, the long-term savings in labor costs and increased productivity offer a significant return on investment.
6. Selecting the Right Welding Rotator
– Assessing Your Needs
Key Factors to Consider: Determine the type and size of workpieces, load capacity requirements, and the level of automation needed.
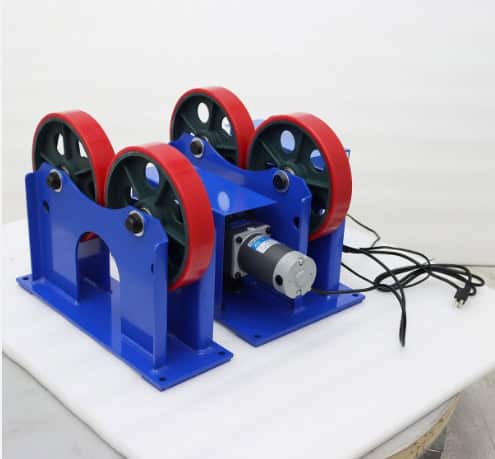

– Evaluating Suppliers
What to Look for in a Manufacturer: Check for reliability, product range, customization options, and after-sales support.
– Customization Options
Tailoring Rotators to Specific Requirements: Many manufacturers offer customization to meet specific industry needs, ensuring the rotators fit seamlessly into your production process.
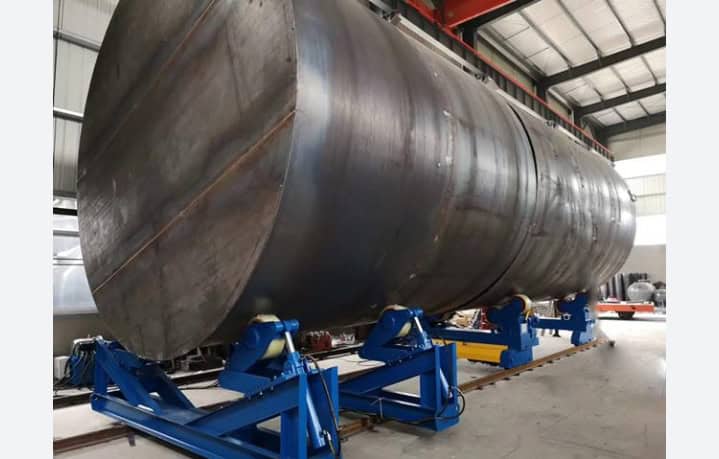

7. Maintenance and Troubleshooting
– Routine Maintenance Practices
Ensuring Longevity and Optimal Performance: Regular inspections, lubrication, and part replacements are essential for maintaining the performance of welding rotators.
– Common Issues and Solutions
Troubleshooting Tips for Common Problems: Addressing issues like uneven rotation, roller wear, and control system failures promptly can prevent downtime.
– Upgrades and Replacements
When and How to Upgrade Your Equipment: Assess the condition of your current equipment and consider upgrades or replacements to enhance performance and productivity.
8. Future Trends in Welding Rotators
– Technological Advancements
Innovations in Control Systems and Automation: Developments in control technologies and automation are making welding rotators more efficient and user-friendly.
– Industry Demands
Emerging Needs in Different Sectors: As industries evolve, the demand for more versatile and capable welding rotators is increasing.
– Sustainability and Efficiency
Trends Toward Eco-Friendly and Energy-Efficient Solutions:** The focus on sustainability is driving the development of energy-efficient rotators with reduced environmental impact.
9. Conclusion
– Summary of Key Points
Recap the importance of welding rotators, their types, applications, and benefits.
– Final Thoughts on the Importance of Welding Rotators in Modern Fabrication
Emphasize the critical role of welding rotators in improving productivity, safety, and weld quality across various industries.